Emission Systems
Caveat: The various systems described here and on linked pages are generic in nature and NOT specific to a particular make/model of Chevrolet. You need to consult your Chevrolet's service manuals for particulars.
Prior to emission standards, the crankcase was vented to the atmosphere.
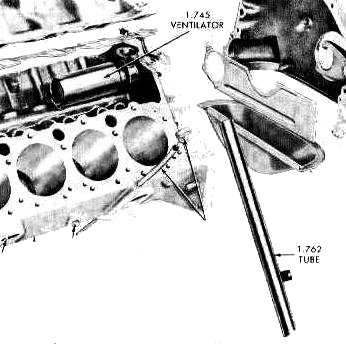


Draft tube and ventilator on an early small block Chevrolet V8 engine.
The ventilator was attached to the engine block under the intake manifold
to collect crankcase fumes and was vented to the outside atmosphere
via the draft tube.
To satisfy the state of California emission requirements, in 1961 the Air Injector Reactor (AIR) system was introduced. Striving for even further reduction of emissions, Chevrolet introduced the Controlled Combustion System (CCS) in 1968. Systems that prevent distributor vacuum advance in low gear were introduced for the 1970 model year. They are the Transmission Controlled Spark (TCS) and the Combined Emission Control (CEC) system. The exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system was developed to control the oxides of nitrogen (NO2) exhaust emission. The EGR system introduces inert exhaust gases into the combustion chamber to lower combustion temperature, thereby reducing the formation of NOx which increases as combustion temperatures increases. This system was introduced in 1973.
Engine operation is not the only contributor to emissions. The simple evaporation of fuel tank contents is also a source of emissions. When combined with the atmosphere and sunlight, these fuel vapors form photochemical smog. in 1970, Chevrolet introduced the Evaporation Control System (ECS). This system seals the fuel tank to capture the fuel vapor for storage in a charcoal canister. Through manifold vacuum, the canister is purged of the vapor during the operating modes of the engine. The vapors are introduced and burned in the combustion process.
Over the years various attempts have been made to control exhaust emissions. In 1958 the Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system was introduced as standard equipment on the 348cid Chevrolet engines in heavy trucks.
In 1966, California introduced stricter emission standards for vehicles built in (or to be sold in) the state. Thus, the Air Injection Reactor (AIR) system was born.
An alternative to the A.I.R. system, the Controlled Combustion System (CCS) introduced in 1968 on some engine/transmission combinations was used.
In 1968, Chevrolet introduced the Carburetor Heated Air (CHA) system to help improve fuel economy and eliminate carburetor icing.
The Transmission Controlled Spark (TCS) system was introduced in 1970 and had some variances in 1971 and 1972.
First introduced in 1970 for vehicles sold in California, the Evaporation Control System (ECS) was mandated in 1971 for all cars and trucks under 6,000 pounds to be equipped with such a system.
The data from the links above are from Chevrolet's "Emission Control Systems."
© ChevelleWorld

 1964 Chevelle
1964 Chevelle 1965 Chevelle
1965 Chevelle 1966 Chevelle
1966 Chevelle 1967 Chevelle
1967 Chevelle 1968 Chevelle
1968 Chevelle 1969 Chevelle
1969 Chevelle 1970 Chevelle
1970 Chevelle 1971 Chevelle
1971 Chevelle 1972 Chevelle
1972 Chevelle


